Minimum Processor State is a power setting that lets you change the minimum processor usage value. You should set the minimum processor state to a lower value so that the processor uses minimum resources when it is performing minimal tasks, inactive or idle. This results in the CPU consuming less power. However, there is much more to the minimum processor state and how it affects the CPU usage, power consumption, and heat generated. This article addresses a few queries about Windows’s minimum processor state setting and its optimal value.
What Is Minimum Processor State in Windows?
The minimum processor state refers to the amount of processing power a CPU is directed to use when the system is idle or under low stress. The minimum processor state value in power options lets you change the percentage value that determines the minimum operating frequency of the CPU. If you set the minimum processor state value to 15%, the CPU will not go below 15% processor usage. But this entirely depends on the device you use. When you change the minimum processor state value, you can not only control the power consumption, i.e., voltage and current, but also CPU core temperatures and clock speed. You can lower the minimum processor state to lower CPU temperature if you are facing higher CPU temperature even when idle. However, if you are running a processor-intensive application, and you see a dip in performance due to processor thermal throttling, increasing the minimum processor state value will bypass the thermal throttling. Depending on the process you are currently running, you can either increase or decrease the minimum processor state value. Since minimum and maximum processor state directly contributes to the change in system temperature, setting a lower minimum processor state also lowers the CPU fan’s RPM when idle, and increasing the value increases the fan’s RPM. One disadvantage of lowering the minimum processor state value is that it may decrease system performance. If that’s the case, you can slightly increase the minimum processor state. However, we only recommend setting the value to between 5%-15%.
How Does Minimum Processor State Value Affect Performance?
When you set a lower minimum processor state value, the CPU usage will not go below the set percentage. This is a good configuration if you want to improve your CPU component’s lifespan. However, this can lead your system to have a choppy performance when running processor-intensive application. When you run an application that uses quite a lot of processor resource, its temperature will increase, resulting in higher CPU fan RPM to cool the processor. But if the CPU starts to thermal throttle and the minimum processor state value is low, the system will use lower processor resource. This means the low processor resources for the application, which will not perform as efficiently as it used to. This is where increasing the minimum processor state value comes in. When you have a higher minimum processor state value and the CPU starts to thermal throttle, the power settings will not let CPU usage go below the minimum processor state value. Even if the CPU thermal throttles, the system cannot limit the usage of processor. This implies that, the processor-intensive application which suffered when setting a lower minimum processor state value will work pretty smoothly if you increase the value. However, this does come with a few disadvantage like decreased processor and CPU fan life span, or the system may suffer from cooling issues due to dried-up thermal paste or abrupt shutdown because of overheating.
How to Change Minimum Processor State?
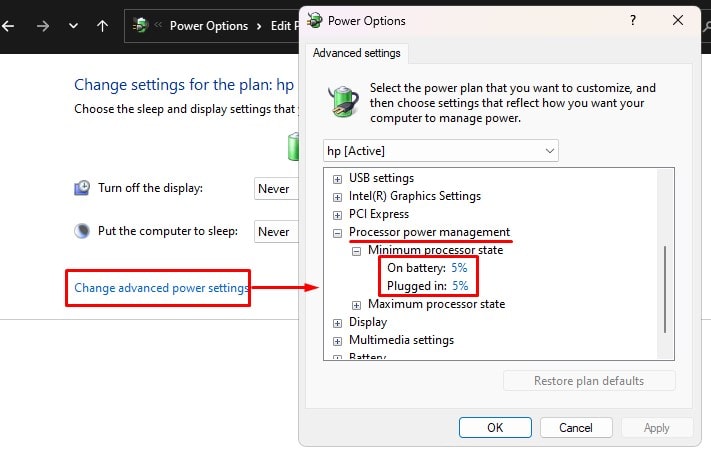
By default, Windows sets the minimum processor state value as 5%. But you can change its value according to your choice. Although you can select the minimum processor state to any value of your choice, make sure that you do not set a high percentage value. If you set the minimum processor state to a higher value, suppose 70%, your CPU will use higher processor resources even on idle. By doing this, the system does not let the CPU run below 70%. So, if the CPU starts to thermal throttle, it will use 70% of the processor at the least, providing more resources. However, this might result in constant power consumption and increased CPU temps. And, the CPU fan will constantly spin at a higher RPM, which never a good sign.
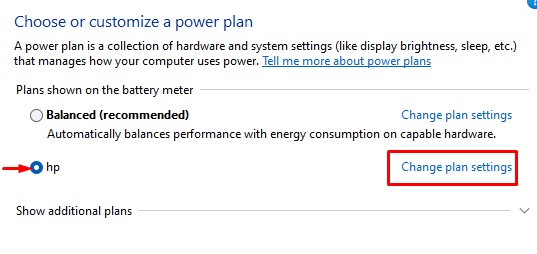
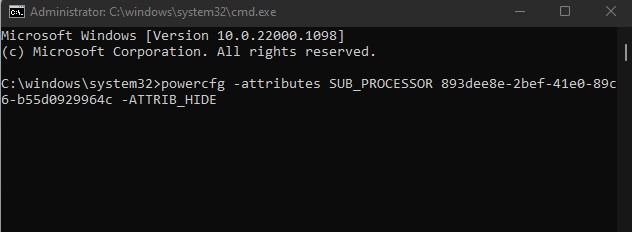
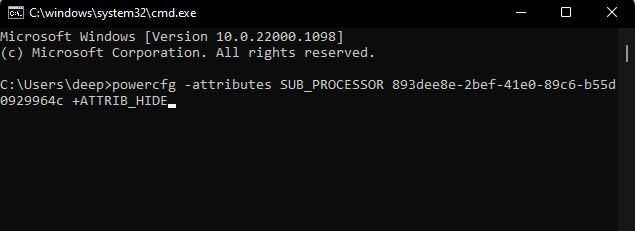
Add/Remove Minimum Processor State
If you cannot find the minimum processor state in power options, you need to make the setting visible using Command Prompt. Below we have explained the steps to add and remove minimum processor state in Windows
What is the Ideal Minimum Processor State Value?
The default value for minimum processor state is 5%. However, depending on the type of system you use, this value can vary. Meaning that, if you are on a desktop, the base frequency that the processor can use to operate the entire system is about 20%. So, setting the minimum processor value to minimum operating frequency will not make any sense as the processor will constantly use 20%. For desktop, you can set this value to 20%-30%. However, in case of laptop, the base frequency to operate the system is very low compared to desktop. Therefore, you can set this value as low as 5% for laptops. But if you are running a heavy application, you can increase this value to 50% to increase its performance. The CPU will constantly use higher resources if you have a higher minimum processor state value, even when the system is idle. This means higher CPU temperature and constant CPU usage. Therefore, you can stick with the default 5% as the minimum processor state value. However, if your system suffers from lags when running processor-intensive application, you can slightly increase this value to improve CPU performance.
Does Lowering Minimum Processor State Save Battery?
Your CPU will run on a lower voltage when you lower the minimum processor state value. This means the power consumption is also low, thus increasing battery life. However, we do not recommend that you set the value to 0. Although your battery life will improve, the CPU performance may decrease if you set the minimum processor state to 0.