From ball mice that use mechanical precision, optical mice that use light sensing technology, to wireless mice that use radio frequency. The computer mouse may look plain and unassuming, but it is not so simple. There’s an interesting insight into how it actually works. So, in this article, we explain the different types of mice and how each of them works.
What is a Computer Mouse?
A computer mouse is a pointing device for easy navigation of any a PC’s graphical user interface. In a nutshell, a mouse is a device you use to move the mouse pointer around. Almost all mice are used for two-dimensional navigation on a flat surface. However, the advancement of technology has introduced us to the likes of 3D mice and Gyroscopic mice. The mouse is named so because it resembles an actual mouse.
Different Types of Mouse and How They Work
While the functions of a mouse do not vary much, there are several different types. Some of them use different technologies, and some have different features. Here are all the different types of mice and how they work.
Ball Mouse
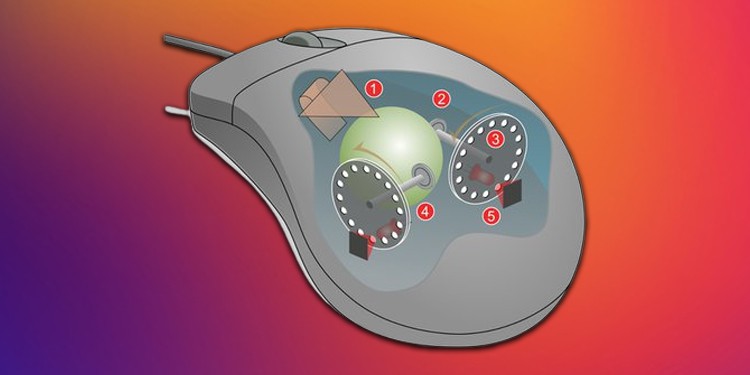
A ball mouse is a type of mouse that uses a rubber ball to track a user’s hand movement to move the cursor. It is one of the very first kinds of the mouse. Furthermore, the name mouse was also based on an early model ball mouse that used to have a wire cord on its rear. The ball mouse works by rolling a ball at the bottom of the mouse after it comes in contact with the surface. As the user’s hand moves, the ball rolls in different directions, and the mouse hardware pick it up. The mouse knows where the ball is rolling and how far it is rolling by two wheels that spin as the ball rolls. If the ball rolls forward, one of the wheels also spins with it. The other wheel is oriented so that the wheel spins when the ball rolls to the side. If the ball rolls diagonally, both of the wheels spin simultaneously. The wheels are shaped like a gear with all its teeth covered, leaving small holes along its perimeter. The mouse internal has a LED light that shoots light through the hole of the wheel to the other end, where there is a detector. Whenever the wheel moves, the gear teeth shape in the wheels blocks the light and rejoins whenever the wheel holes align again. This causes the light to break and reform as the wheel moves continuously. The more the light flickers, the more distance the mouse has moved. The faster the light flickers, the faster the mouse has moved. The detector detects it all and sends the information to the computer to move the cursor.
Optical and Laser Mouse
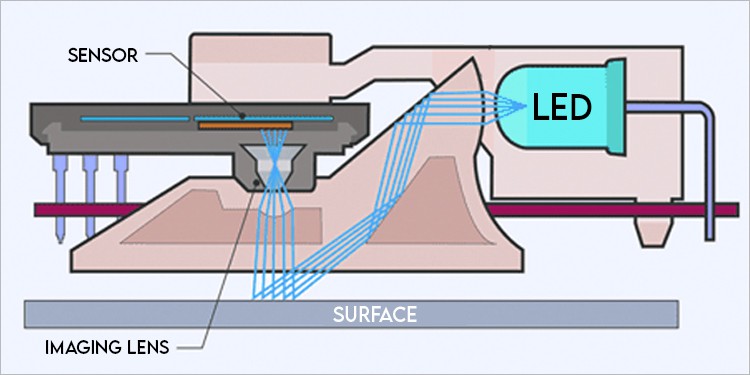
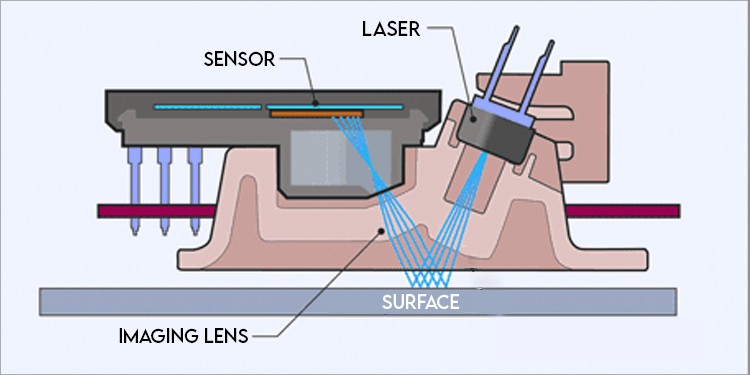
Optical and laser mice work similarly, but their light sources differ. An optical mouse uses LED light to determine the mouse movement, while the laser mouse uses a laser. The optical mouse is the most popular and works by shooting rays of light to a plain surface. The light rays then bounce off the surface, and the mouse sensor picks them up. The sensor captures more than 1000 images of the surface per second and compares the images to know where the mouse moved. Laser mice do the same but use a laser instead of an LED light. So, the laser mouse works better on some surfaces than an optical mouse. An optical mouse doesn’t work on glass as all the light passes through the glass. However, laser mice work on glass surfaces as lasers are much more powerful, and some of the light manages to bounce back.
Wireless Mouse
As the name suggests, a wireless mouse doesn’t have wires and cords. It uses Bluetooth and other technology to send the information of where the mouse moved. For tracking where the mouse moved, most wireless mice use optical technology. A Bluetooth mouse directly connects to a computer’s Bluetooth, but a 2.4Ghz wireless mouse has a USB dongle. The dongle must be plugged in for your mouse to connect with your computer through radio frequency technology. A Bluetooth mouse is free of that but also experiences slightly more latency. Most wireless mice use 2.4 GHz radio frequency, but there are even more powerful 5 GHz frequency mice available.
3D Mouse
A 3D mouse is a complementary mouse that is mostly used to manipulate 3D objects. It doesn’t replace the regular mouse and is usually on your off-hand to position 3D models. The 3D mouse is mostly used by professionals for 3D model designing. The 3D mouse looks like a bottle cap, and you move that around to manipulate objects in 3D space. The 3D mouse works like a joystick but supports movement along its six-axis due to its multi-axis sensors.
Inertial and Gyroscopic Mouse
Usually called an air mouse, the inertial and gyroscopic mouse allows you to operate your computer by moving the mouse around in the air. It is generally used for virtual gaming. The gyro mouse is also used for playing interactive fitness games. You can control your mouse pointer with a gyro mouse from a distance of 10 meters. The gyro mouse works with its two gyro motion sensors that allow it for three-dimensional navigating. Gyro motion sensing technology is the same as how you can control some mobile game with the tilt of your device.
Other Specialty Mice
Some unique mice are technically considered mice, but they look far from the regular mouse. Here are some of the more unique types of mice.
Trackball
A trackball is a mouse pointer device with a ball sticking out its top. While it looks only remotely similar to a mouse, a trackball is technically considered a mouse. Furthermore, the trackball was created before the regular mouse and was also an inspiration for the ball mouse. The trackball has a ball jutting out its top, and you move that ball around with your finger to use it. It works on the same principle as a ball mouse, but modern-day trackballs use advanced sensors to track your finger movement.
Pen Mouse
Pen mouse combines optical and wireless mouse features in an oddly shaped mouse. The working principle of a pen mouse is the same as an optical and wireless mouse. It uses led light to take and compare the images of the reflected light of surfaces. Furthermore, a pen mouse also uses a special technology like a wireless mouse. Similarly, it mainly uses 2.4 GHz frequency and also has a dongle. After you plug the dongle, your pen mouse should connect to your computer using 2.4 GHz radio frequency.